Double-Sided Configuration for Maximizing Rooftop Solar Production
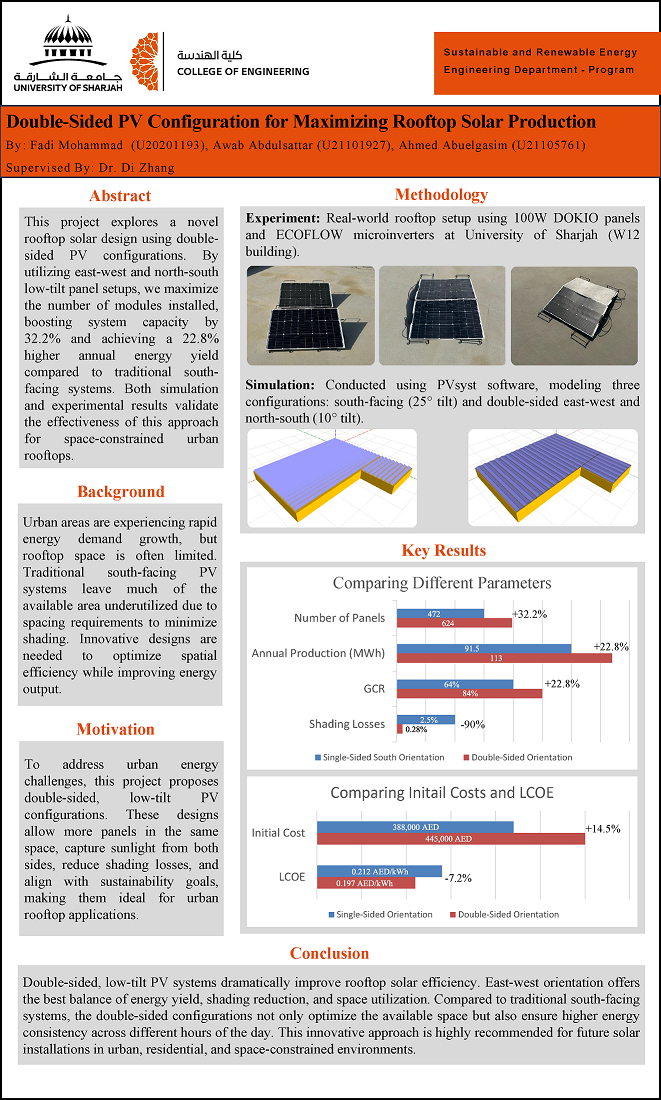
This project investigates low-tilt dual-tilt photovoltaic (PV) configurations, arranged in east–west and north–south orientations, as an alternative to conventional single-tilt south-facing systems. Using PVsyst simulations and experimental validation on the University of Sharjah rooftop, the dual-tilt layouts allowed 32.2% more modules to be installed within the same area, increasing system capacity from 47.2 kW to 62.4 kW. Annual energy yield improved by 22–23% while shading losses were reduced by up to 92%. The use of lightweight flexible modules further reduced installation costs and enabled denser packing without compromising performance. These results highlight dual-tilt PV systems as a highly effective design strategy for maximizing rooftop solar potential in space-constrained urban environments.